Revision of surgical interventions
Revision of interventions
At the Rizzoli Orthopaedic Institute in Bologna, Dr. Roberto Bevoni specialises in specialised foot and ankle surgery, including complications from surgical treatments performed at other facilities.
Among the most common issues are:
- Recurrence of hallux valgus (bunions)
- Metatarsalgia from foot forefoot correction
- Outcomes of minimally invasive surgery
- Infections of the forefoot following interventions
- Pseudoarthrosis of the forefoot and hindfoot
- Achilles tendon infections
- Outcomes of corrective surgery for flat or cavus foot in both children and adults
- Revision of ankle prostheses
- Revision of joint fusions
Corrective foot surgery doesn't always yield positive results. Patients undergoing surgical procedures are informed by medical personnel that the final clinical result may not always meet the patient's expectations.
The intervention doesn't always completely solve the problem for which the patient consulted the doctor, and in some cases, the result can even be worsened.
The doctor always does their best to achieve a good outcome, but both national and international cases report failures.
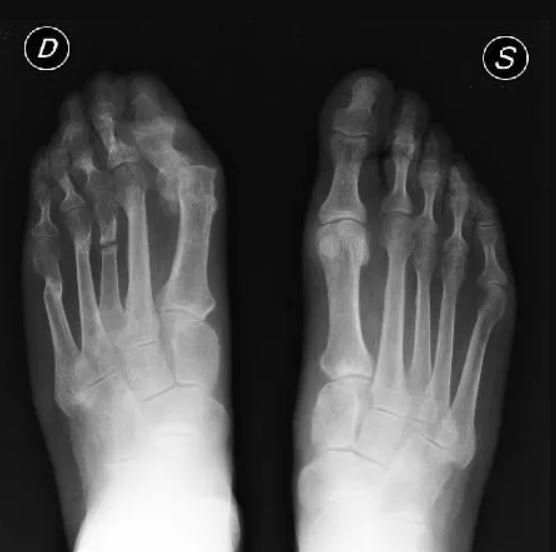
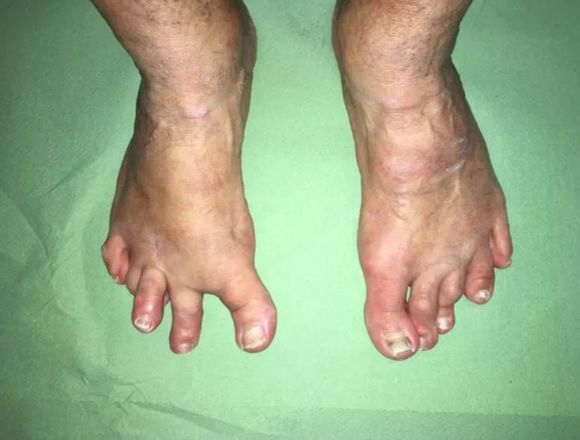
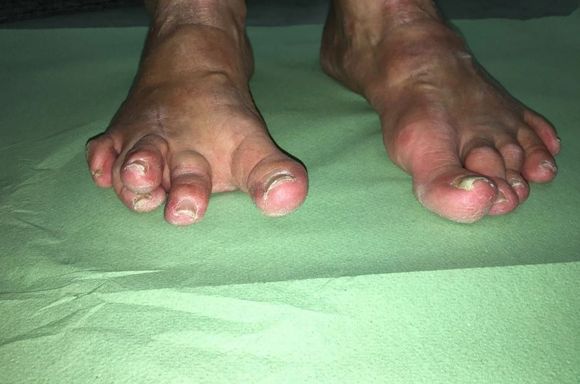
Particularly in foot surgery, it's quite common to encounter patients complaining of pain after corrective bunion surgery, given the high number of patients undergoing this procedure. The most common reason for the onset of pain is transfer metatarsalgia, followed by recurrence of bunions and, to a lesser extent, deformity of the other toes.
Approximately 25% of patients can be treated with conservative measures, including orthotic insoles, the use of silicones, or corticosteroid injections.
However, in the remaining 75%, finding a non-surgical solution is challenging.
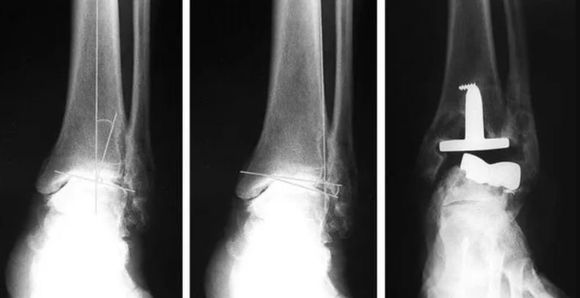
Revision surgery is more complicated than the initial procedure because the anatomy has been altered by the previous surgery. There are often conditions that make the surgeon's work more difficult, such as poor bone quality, lack of an important bony segment, cartilage degeneration, scar retractions, and other complications involving the soft tissues of the foot or ankle.
Various reviews of revision cases make it clear that mediocre surgical results and the need for further surgery could be prevented by selecting surgical techniques that avoid joint destruction, excessive shortening of individual metatarsals, and digital amputation.
However, the poor outcome is not always attributed to the surgeon's error; sometimes, clinical conditions such as diabetes, inflammatory arthropathies, or immune deficiencies can compromise the surgery's outcome.