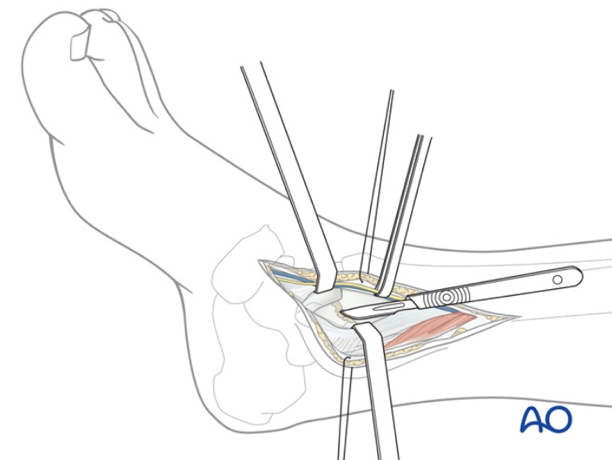
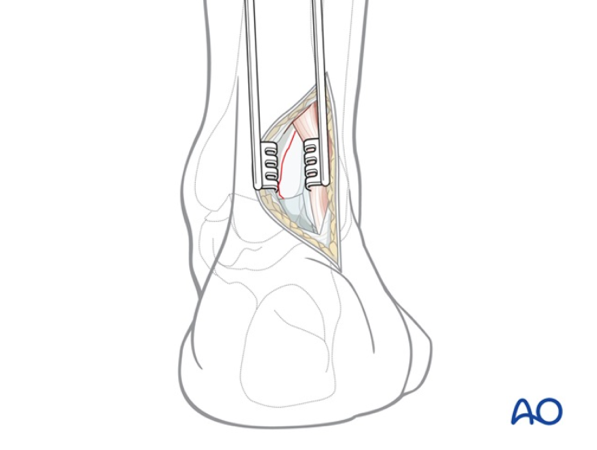
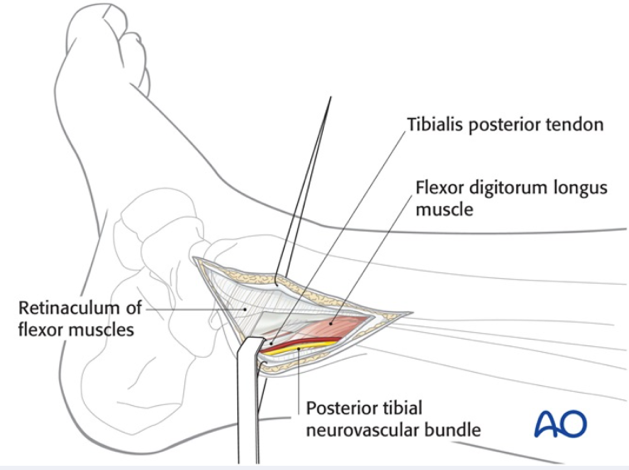
Ankle Fractures
Ankle Fractures
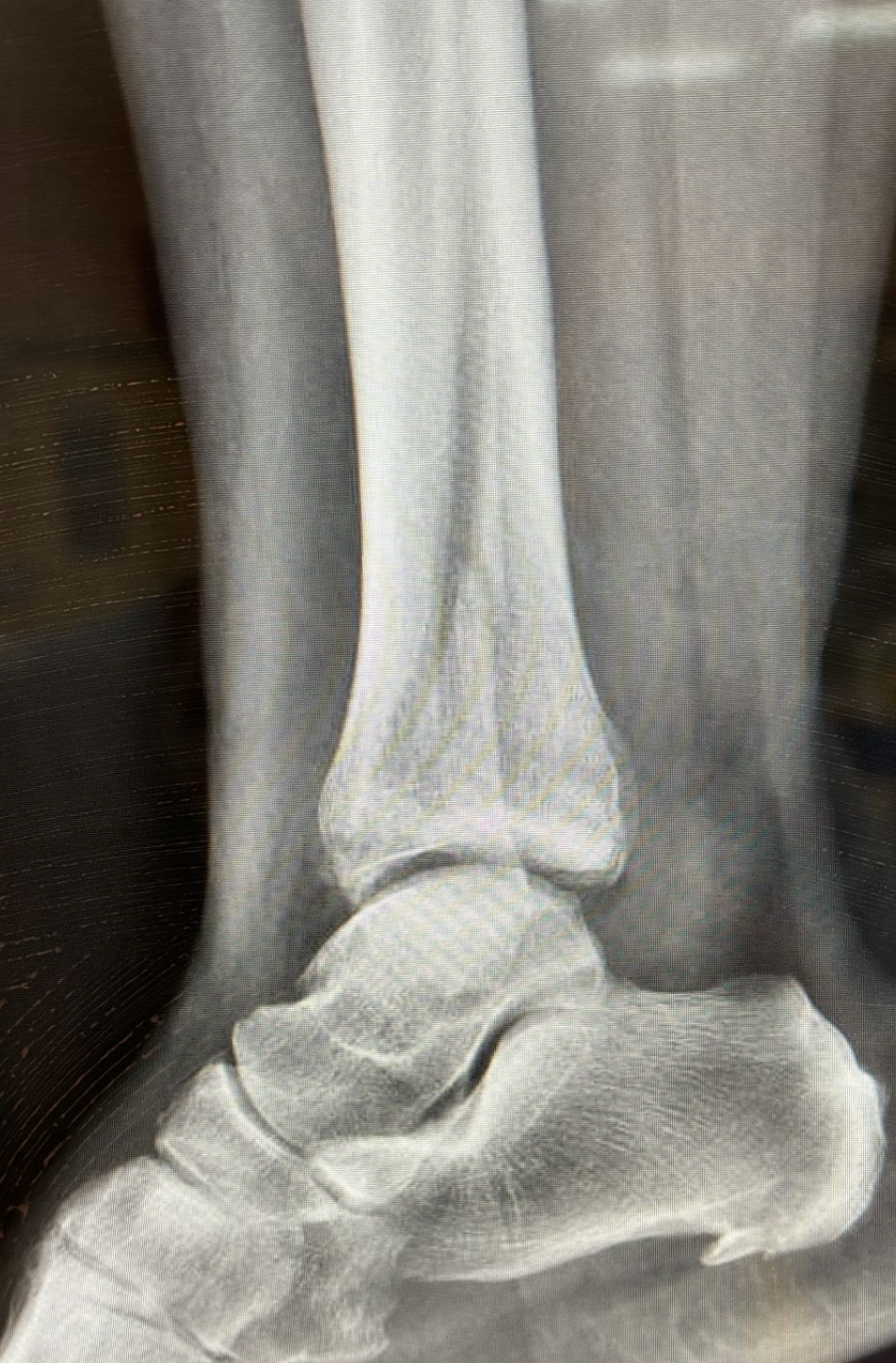
Ankle fractures range from small bone fragments to displaced fractures and occur in approximately 0.15% of the population (150 people per 100,000 annually), most often due to high-impact trauma or twisting injuries to the ankle joint.
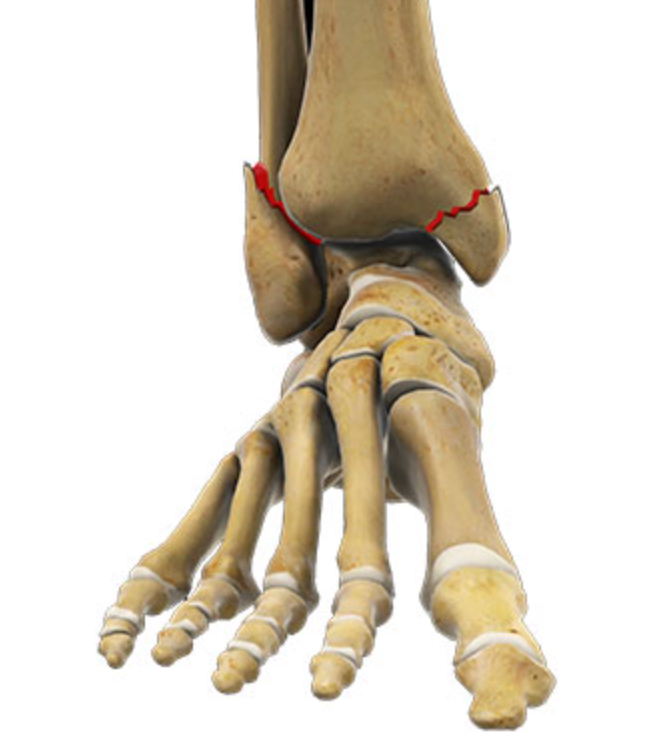
The ankle joint is made up of the tibia, fibula, and talus. The lower ends of the fibula and tibia connect and rest on the talus, which serves as the main link between the leg and foot.
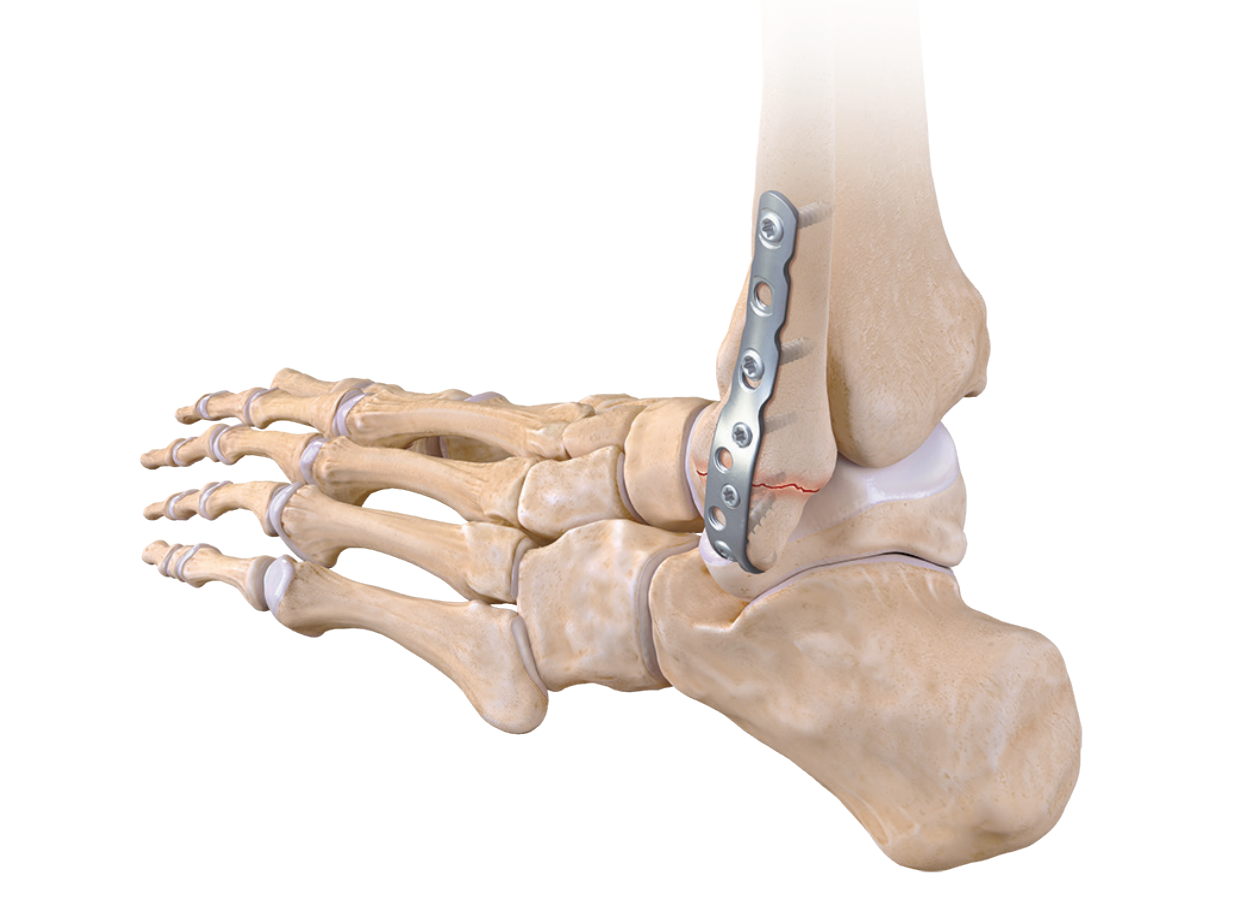
Ankle fractures can involve one or more bone segments. Some fractures, if stable or minimally displaced, can be treated non-surgically with a brace or cast. Displaced fractures or those involving multiple bone segments are more severe and require surgical intervention.
Fractures can be either open or closed. In closed fractures, the skin remains intact, while in open fractures, a bone segment punctures the skin, allowing bacteria or other pathogens to come into contact with the bone.
Symptoms and Causes
How can I tell if my ankle is broken?
It is not always easy to determine whether ankle pain is caused by a sprain or a fracture. For this reason, it is advisable to visit an emergency room and undergo an X-ray.
Common symptoms of a fracture include:
Severe pain in the ankle.
Difficulty bearing weight on the ankle.
Pain when touching the ankle.
Redness and bruising with discoloration compared to the natural pink skin tone.
Swelling with localized or widespread enlargement of the joint.
Can I walk with a broken ankle?
Walking with a broken ankle is difficult and painful. Additionally, attempting to walk could worsen the fracture or damage the tendons and ligaments supporting the ankle.
How do ankle fractures occur?
Ankle fractures typically result from three mechanisms:
- Direct trauma
- Twisting injuries
- Falls from height
- Crushing injuries
Can an ankle sprain cause a fracture?
An ankle sprain occurs when the tibio-tarsal joint twists, leading to ligament injuries. A twisting injury can also cause an avulsion fracture or a more significant fracture. Some tibia and fibula fractures are associated with damage to the anterior talofibular ligament and/or the deltoid ligament of the ankle.
Are there different types of ankle fractures?
Yes, there are various types of ankle fractures involving one or more bone segments:
Isolated Fractures:
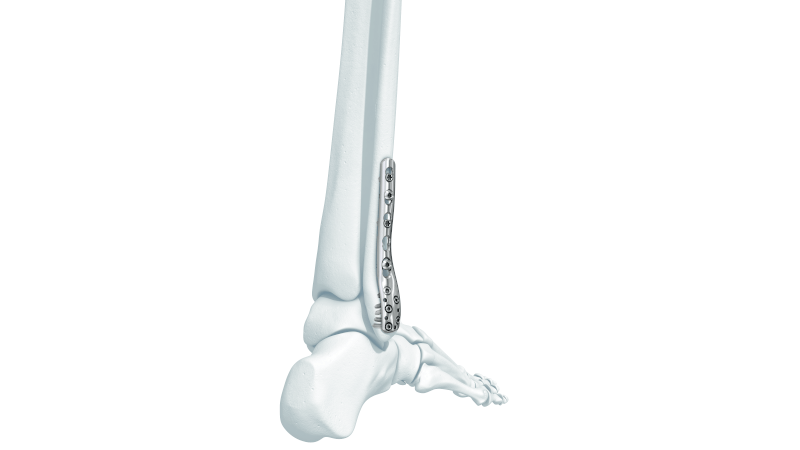
- Lateral Malleolus Fracture: Occurs when the distal portion of the fibula breaks, affecting the outer side of the ankle. This is the most common type of ankle fracture.
- Medial Malleolus Fracture: Occurs when the distal portion of the tibia breaks, affecting the inner side of the ankle.
- Posterior Malleolus Fracture: This occurs when the posterior portion of the tibia breaks. Isolated posterior malleolus fractures are relatively rare and typically result from hyperextension injuries to the ankle.
- Anterior Malleolus Fracture: This occurs when the anterior tubercle of the tibia (Tillaux-Chaput Tubercle) breaks. This type of injury is often associated with damage to the syndesmosis (anterior tibiofibular ligament) and is uncommon.
- Pilon Fracture: The tibia ends in a section called the "roof" of the ankle. When this area breaks, it is referred to as a pilon fracture. This injury usually involves the articular surface of the tibia, affecting the cartilage. It often leads to severe post-traumatic ankle arthritis, even after surgical intervention with good fracture alignment. Pilon fractures may also be associated with fibula fractures.
Combined Fractures:
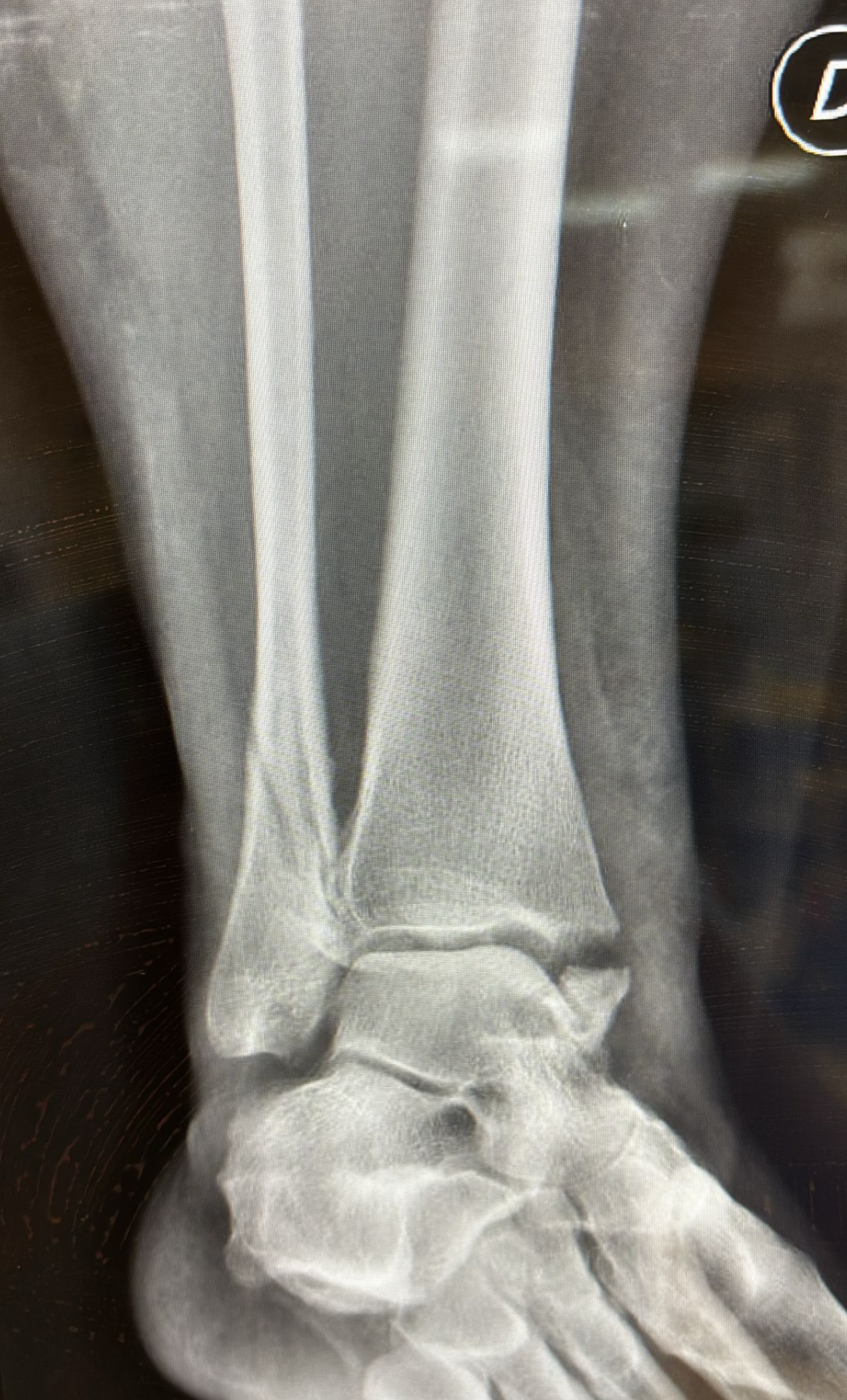
- Bimalleolar Fracture: This occurs when both the distal tibia and fibula are broken. It is the second most common type of ankle fracture.
- Trimalleolar Fracture: In this case, three parts of the ankle are fractured, most commonly involving the tibial malleolus, fibular malleolus, and posterior malleolus.
- Maisonneuve Fracture: This results from an ankle sprain that causes injury to the distal tibiofibular ligament and interosseous membrane, combined with a spiral fracture of the proximal fibula near the knee.
- Syndesmotic Injury: The syndesmosis is a joint between the fibula and tibia, held together by ligaments. A syndesmotic injury occurs when there is at least one fracture in the tibia or fibula along with ligament damage at the syndesmosis.
What is the difference between a stress fracture and a bone fracture?
Tibial fractures can sometimes result from overuse rather than trauma. These stress fractures are common in professional athletes due to repetitive movements that overload the distal tibia.
Management and Treatment
How are ankle fractures treated?
The treatment depends on several factors:
Whether the fracture is displaced or non-displaced
The number of bone segments involved
The degree of comminution (bone fragmentation)
Associated ligament injuries in the ankle
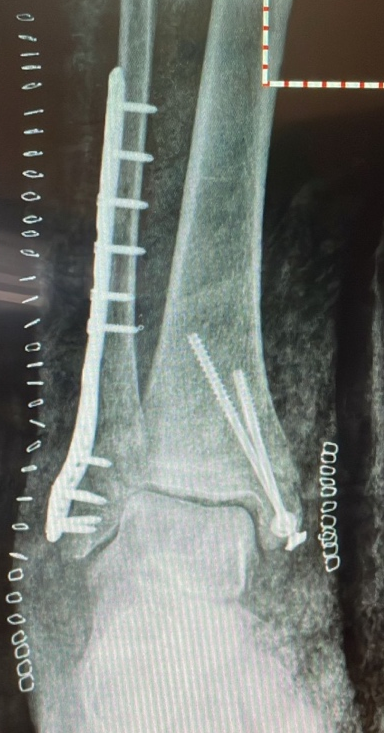
Stress fractures and non-displaced fractures typically do not require surgery and can be treated with a walker boot or cast. Severe fractures require reduction or surgical intervention.
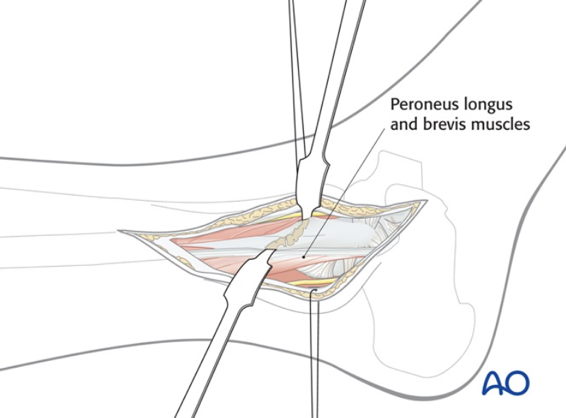
Reduction: This involves realigning the fractured ankle and must be performed in the Emergency Room in cases of displaced fractures or ankle dislocations.
What happens before the surgery?
Before surgery, the patient is evaluated by an orthopedic surgeon and an anesthesiologist to assess ongoing therapies, which may need to be paused or adjusted before the procedure.
To prepare for anesthesia, you should:
- Avoid food and drinks for eight hours before hospitalization unless instructed otherwise.
- Quit smoking at least two weeks prior to the surgery to improve heart and lung health.
What are the possible complications after ankle fracture surgery?
Complications may include:
- Acute Compartment Syndrome (ACS): Pressure builds up in the muscles, restricting blood flow to muscles and tissues. This can cause permanent damage to muscles and nerves.
- Delayed Union: Bone healing takes longer than normal.
- Nonunion: The fracture fails to heal within six months of the trauma.
- Malunion: The bone heals with improper alignment, leading to residual deformity and functional impairment.
- Bone Infection (Osteomyelitis): Infection of the bone, more common in open fractures.
- Nerve or Blood Vessel Damage: Ankle fractures can temporarily or permanently damage nerves and impair blood vessels.
How long does it take to recover from ankle fracture surgery?
Ankle fractures can take significant time to heal, with recovery dependent on the severity of the injury.
- Post-surgery, a cast is worn for 30 days without weight-bearing.
- After 30 days, the cast is replaced, and partial weight-bearing of about 20 kg is allowed.
- After 60 days, the cast is removed, X-rays are performed, and a walker boot is provided. Rehabilitation begins, with gradual weight-bearing of about 50 kg for another 30 days.
Rehabilitation exercises may include hydrotherapy, elastic band exercises, magnetotherapy, cycling, and proprioceptive balance boards. Full weight-bearing is generally resumed within
3 months of surgery, but complete healing can take up to
18 months.
When should I contact my doctor or visit the Emergency Room after surgery?
You should seek medical attention if you experience:
- Uncontrolled pain inside the cast
- Numbness or tingling associated with pain
- Increased swelling
- Fever above 38°C (100.4°F) lasting more than three days
- Signs of infection such as fever, chills, redness, or drainage from the wound
- A new injury involving the operated ankle